
Mistral Launches “Codestral Embed”: AI Code Model Outperforming OpenAI’s Own
Mistral, the French company active in the AI sector, has announced the launch of “Codestral Embed,” its latest innovation in code embedding models.
The company stated that this new model offers performance superior to prominent competing models in the market and opens new horizons in code information retrieval applications.
However, it also sparked important discussions about the necessity of open-weight models to ensure the sustainability of investments in this rapidly accelerating technological field.
Codestral Embed’s Performance and Capabilities
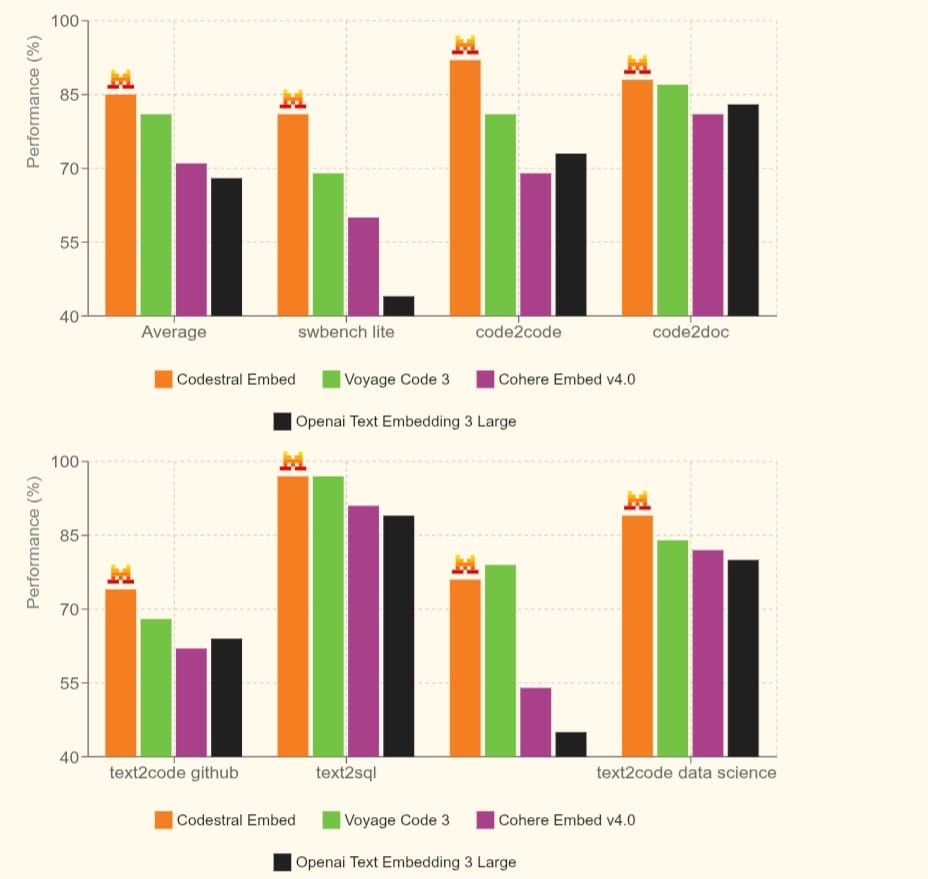
Mistral reported that “Codestral Embed” surpasses well-known models such as “Voyage Code 3,” “Cohere Embed v4.0,” and even OpenAI’s large embedding model in its performance.
These claims are based on results from industry-standard performance benchmarks, most notably “SWE-Bench.”
The company highlighted the model’s ability to produce embeddings of various dimensions and precision, while maintaining strong performance even when using fewer dimensions and the “int8” format to reduce storage costs.
This flexibility seems to be based on a technique known as “Matryoshka embeddings,” where dimensions are ordered according to their importance. Such approach gives developers the ability to choose the optimal balance between retrieval quality and associated storage costs.
How to Benefit from the Model
Regarding how to utilize “Codestral Embed” in practice, the model was primarily designed to help programmers quickly and easily find the code snippets they need, and to understand the meaning of these codes more deeply.
For instance, the model can assist in writing code, suggesting modifications, or even explaining how code works, leveraging its ability to retrieve information from a vast amount of programming examples.
Additionally, users can search for specific parts of code using natural language or the programming language itself, and the model will understand the intent and find suitable results.
It also contributes to detecting similar or duplicate codes within projects.
Another useful application is its ability to group codes that are similar in function or structure, which is beneficial for understanding the composition of large software projects and discovering common patterns within them.
Accessing Codestral Embed
The new model is available to developers through a dedicated Mistral API, under the designation codestral-embed-2505.
The company has set a usage cost of $0.15 per million data units (tokens), with a discount provided for large-volume usage.
In this context, while this price may seem reasonable to some for not having to run the model on their own devices. This particular cost-saving method has drawn some remarks from industry observers.
Some believe that complete reliance on closed APIs could put investments made in processed and stored code data at risk, especially if the developing company decides to discontinue API support or faces challenges leading to its market absence.
It is believed that making such models available with “open weights” technology, alongside the paid API option, could provide greater assurance to users regarding the sustainability of their investments and their ability to continue working with the model in the future, even if they initially choose to use the paid API for convenience.
Competition in the AI Market
The launch of “Codestral Embed” comes at a time of increasing demand for enterprise-focused embedding solutions, particularly for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications.
With this release, Mistral strongly enters a competitive landscape that already includes closed-source models from giants like OpenAI and Cohere, as well as promising open-source options such as Qodo models.
Mistral has recently intensified its activity with notable releases like Mistral Medium 3 and the Agents API.
Now, it’s “Codestral Embed’s” turn to prove its superiority not only in benchmark performance tests but also in real-world usage scenarios for the company to solidify its position in the AI market.




